New Tech for Island Restoration: Sentinel Camera Traps
We're using a cutting-edge new tool to sense and detect animals in remote locations. Find out how!
Our 2024 Impact Report is live!
Published on
May 20, 2024
Written by
Island Conservation
Photo credit
Island Conservation

This article, written by Island Conservation’s International Legal and Administrative Manager, Carolina Torres Trueba, originally appeared on the website of the our partners at Outreach Network for Gene Drive Research. In celebration of the International Day for Biological Diversity, we’re reproducing it here in full!
By Carolina Torres Trueba, International Legal and Administrative Manager, Island Conservation
May 22 marks International Day for Biological Diversity, an occasion to increase understanding and awareness of biodiversity issues and reflect on the state of biodiversity worldwide. Across regions, biodiversity is declining at an unprecedented and alarming rate, with one million species currently threatened with extinction. Invasive alien species (IAS), defined as species that are not indigenous or native to a particular ecosystem, are a key driver of this decline, affecting fragile ecosystems worldwide. According to findings published by IPBES, they have played a key role in 60% of global plant and animal extinctions.
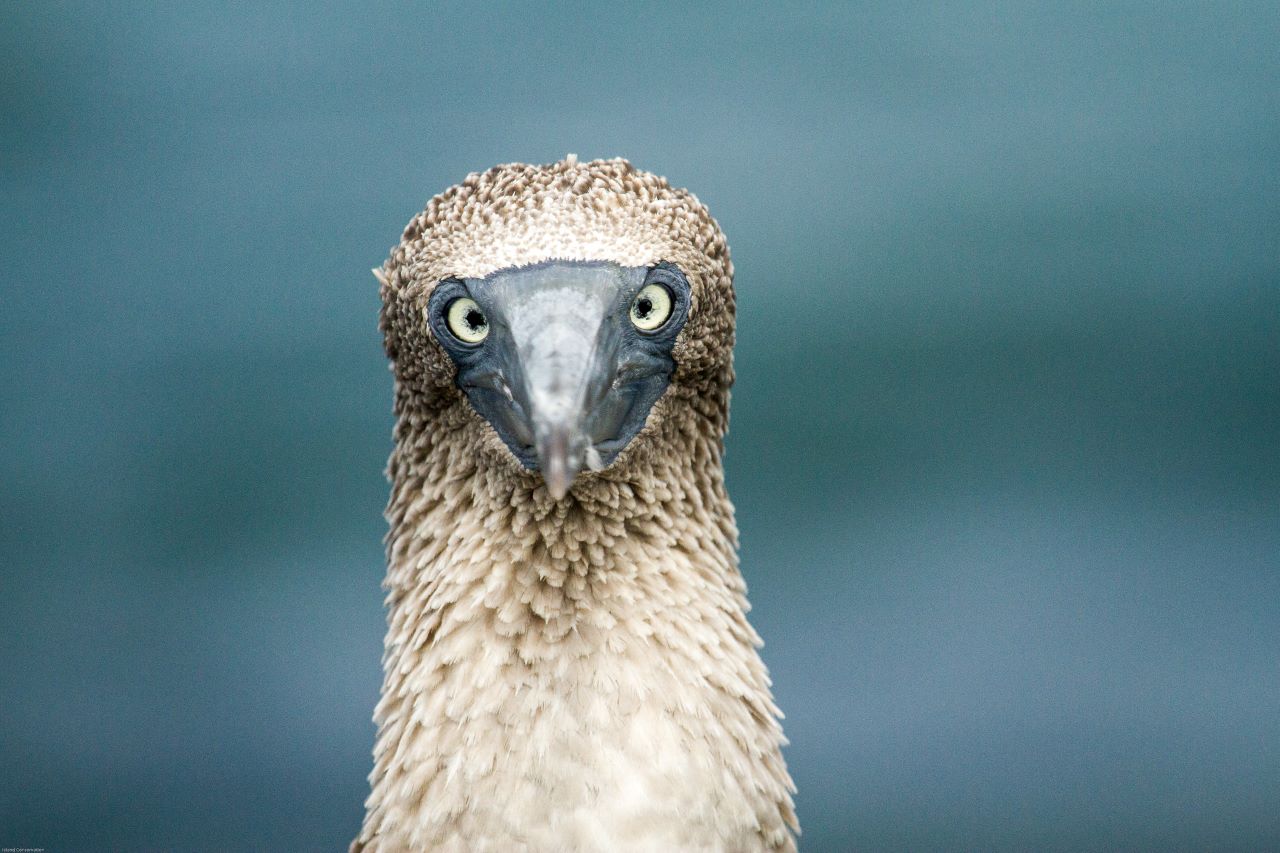

Blue-footed booby on Floreana Island, Galapagos Archipelago, Ecuador. Photograph: Tommy Hall/Island Conservation
As an environmental lawyer and a passionate environmentalist living on the Galapagos islands and working to prevent extinctions and restore ecosystems, I have witnessed firsthand the devastating impact of these intruders on native flora and fauna. Worryingly, the pattern of invasive alien species and the harm they cause is repeated across different regions. From rodents on the Galapagos Islands devouring crops, to brown tree snakes decimating bird populations in Guam, to endangered bird species in Hawaii contracting avian malaria from the bite of invasive mosquitoes, invasive species pose a severe threat to ecosystem stability, economies and human health across the globe.
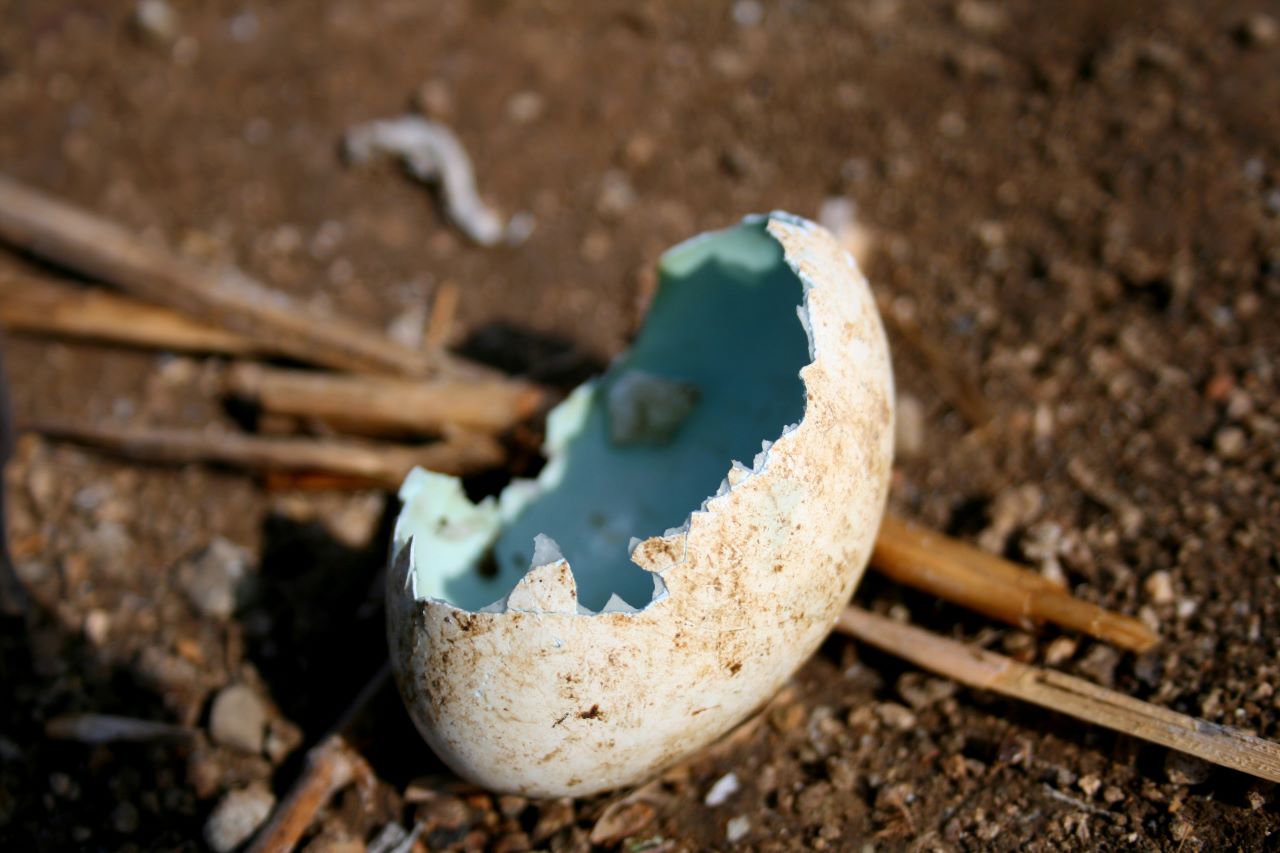

Seabird egg predation by rodents can devastate an island ecosystem. Photograph: Island Conservation
The Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework (GBF) offers a beacon of hope in our battle against biodiversity loss with ambitious goals and targets. However, its successful implementation hinges on our ability to harness the power of research and innovation to address current conservation challenges. Despite global efforts to control invasive alien species, under a “business-as-usual” scenario, their overall number is expected to increase by 36% by 2050 compared to 2005. Current control tools such as trapping or baiting are limited by cost and scale and can have unintended effects on the ecosystem. By investing in transformative technologies and interdisciplinary collaboration, we can develop more effective strategies and tools to address the driving factors of biodiversity loss, including invasive species, and restore balance to our ecosystems.
Synthetic biology stands out as a field which holds great promise. Leveraging the principles of genetic engineering, synthetic biology could offer new tools and approaches to combat invasive species with precision and efficiency. One of the approaches that is currently being explored is the use of gene drive technologies to tackle invasive rodent populations on islands. This approach could complement existing interventions and help tackle the issue of invasive species in a more humane, cost-effective, and scalable manner.
However, with great potential comes great responsibility. As we explore new opportunities within synthetic biology, it is crucial that we proceed with the highest standards possible. Transparency, public engagement, and case-by-case risk assessment must underpin our efforts to ensure that synthetic biology approaches can be harnessed effectively and integrated safely into the conservation toolkit.

Tropical flock in Ngeanges, Palau. Photograph: Tommy Hall/Island Conservation
In addition to synthetic biology, other innovative tools and approaches are also essential for effective invasive species management. From remote sensing technologies, AI, drones, and predictive modeling to citizen science initiatives and community-based conservation efforts, a multifaceted approach is the best way to tackle this complex challenge.
As we celebrate International Day for Biological Diversity, let us recommit to preserving and restoring our planet’s rich tapestry of life. By embracing research and innovation we can turn the tide on biodiversity loss and create a more sustainable and resilient future for generations to come.
Check out other journal entries we think you might be interested in.
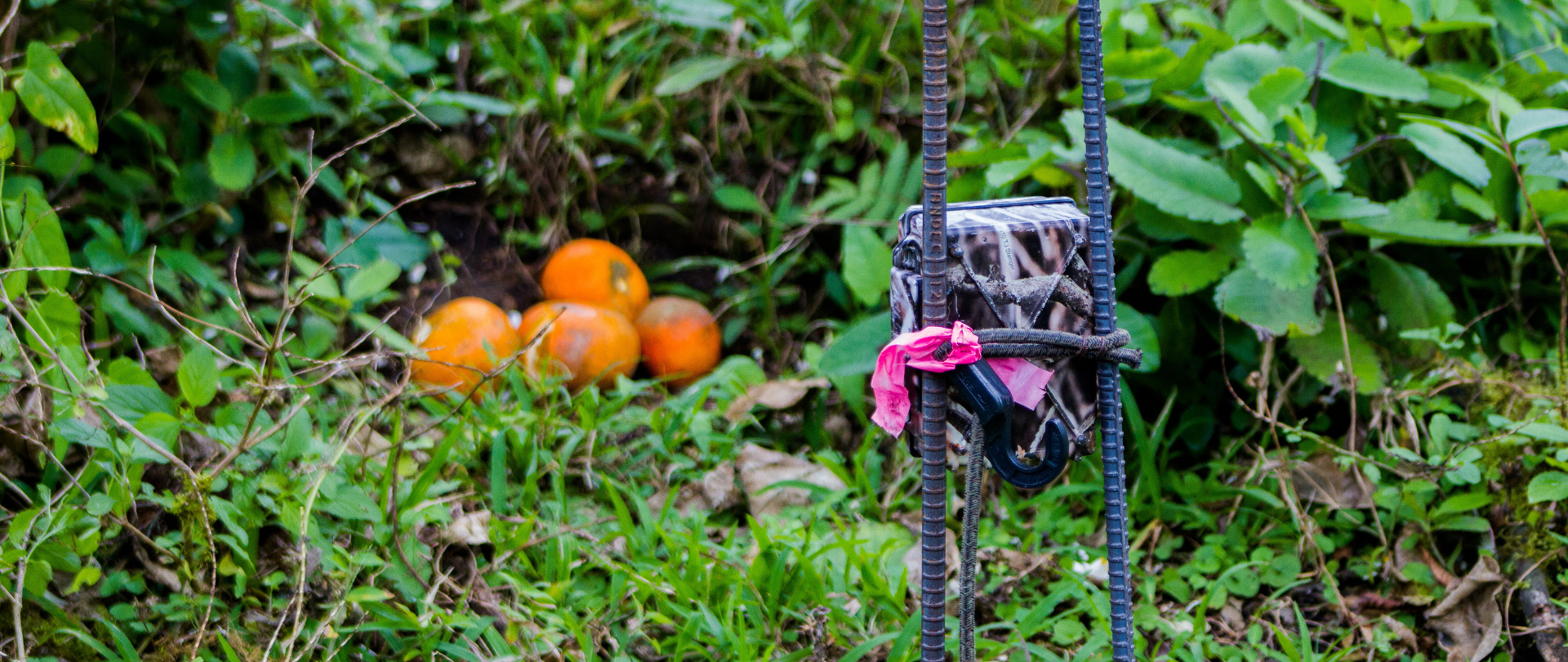

We're using a cutting-edge new tool to sense and detect animals in remote locations. Find out how!

Groundbreaking research has the potential to transform the way we monitor invasive species on islands!

Our team returns from Late Island, Tonga with reports that our conservation actions work! Read notes from our Conservation Impact Director!
Island Conservation turns 30! Three decades of work add up to an immeasurable number of positive impacts.
Investing in new technology and harnessing the power of innovation to save islands is at the core of what we do. Find out how!

Machine learning is helping restore Robinson Crusoe Island! Lenovo's Work for Humankind initiative funds the cutting edge of conservation.

Island Conservation seeks proposals from companies that can provide aerial support in the form of Uncrewed Aerial Systems or Helicopters.

A generous grant from NASA allows us and our partners to maximize the benefits of our island restoration work!

Island Conservation Innovation Team Members and Mississippi State University Researchers Co-Author Scientific Publication on Using New Method to Identify Invasive Species

Island Conservation's GIS Data Science Specialist shares how her experience on Floreana has been shaped by community.