The Ebiil Society: Champions of Palau
Ann Singeo, founder of our partner organization the Ebiil Society, shares her vision for a thriving Palau and a flourishing world of indigenous science!
Our new online shop is live!
Published on
June 22, 2018
Written by
noelle
Photo credit
noelle

Over the past 80 years, the Northern Quoll, a cat-sized carnivorous marsupial with a pointed snout and bushy long tail, had disappeared all over Australia due to the invasive toxic Cane Toad. Northern Quolls used to live across Northern Australia. Their populations started to decrease after the arrival of Europeans, who came with new predators like cats. However, since the introduction of the toxic Cane Toad in the 1930s, populations of the Northern Quoll plummeted as this native marsupial consumed the toxic toad in place of native nontoxic amphibians. To ensure the species’ survival, conservationists worked on relocating the Quoll to several island sanctuaries that are free from predators. Once relocated, they were able to flourish, but a recent study published in Biology Letters suggests that this isolation could have unintended consequences.
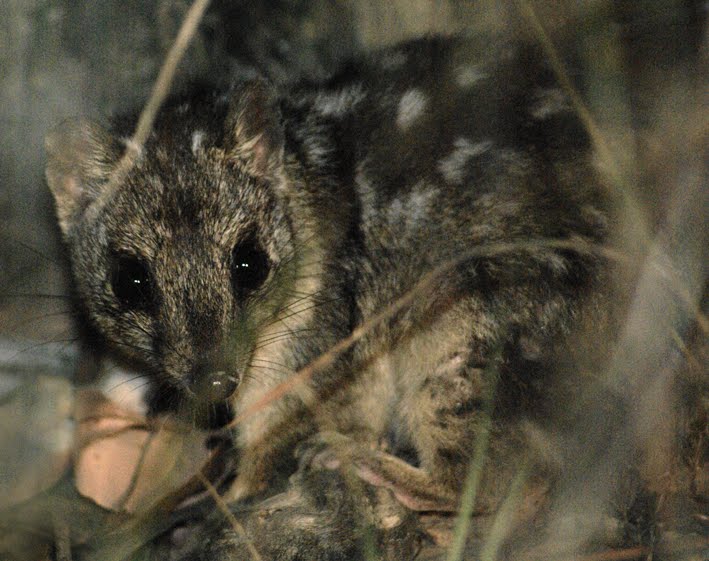

After living in separation from predators for 13 generations, the authors found that the Northern Quoll no longer avoids the scent of even its natural predators. The animals have lost their fear response to predators, making them more susceptible to predation when they are reintroduced to habitats with predators. The mainland Quolls still show a fear response and avoid their top predators such as the Dingo, invasive foxes and feral cats while the isolated ones show no fear at their scent. This study is very important; it shows just how quickly behavior and predator savviness can be lost when living in a predator free sanctuary. Sarah Otto, a theoretical biologist at the University of British Columbia, commented:
This study raises another hurdle faced by conservation biologists trying to save species from the brink of extinction. Breeding programs alter selection and can lead protected species to lose their ability to survive under harsher natural conditions. Reintroduction programs that are staged—selecting first for the most predator-aware of the quolls before release—may be critical to success.
Using this information to select for more predator-aware Quolls to reintroduce back to Australia after being on a predator free island may be part of the solution. Hopefully this new information will help conservationists come up with a more successful protection plan and Quoll populations will be able to thrive once again.
Featured photo: Eucalyptus forests in Australia are important habitats for Quolls. Credit: Brian Gratwicke
Source: Science News
Check out other journal entries we think you might be interested in.

Ann Singeo, founder of our partner organization the Ebiil Society, shares her vision for a thriving Palau and a flourishing world of indigenous science!

This historic agreement aims to protect the marine and coastal areas of the Southeast Pacific.

Our projects to restore key islets in Nukufetau Atoll forecast climate resilience and community benefits in Tuvalu!

Island Conservation and partners have published a new paper quantifying ecosystem resilience on restored islands!

Climate Week NYC: what is it and why is it important? Read on to find out why Island Conservation is attending this amazing event!

With sea levels on the rise, how are the coastlines of islands transforming? Read on to find out how dynamic islands really are!
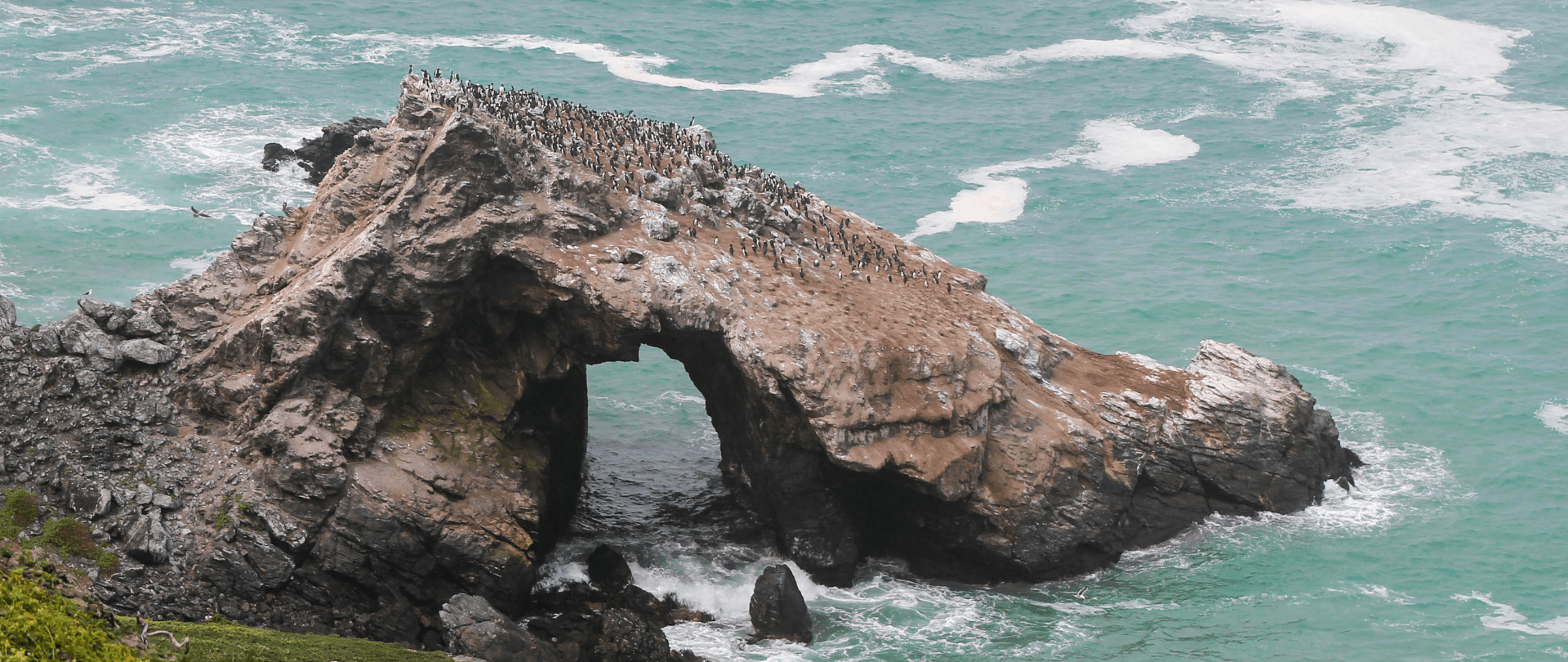
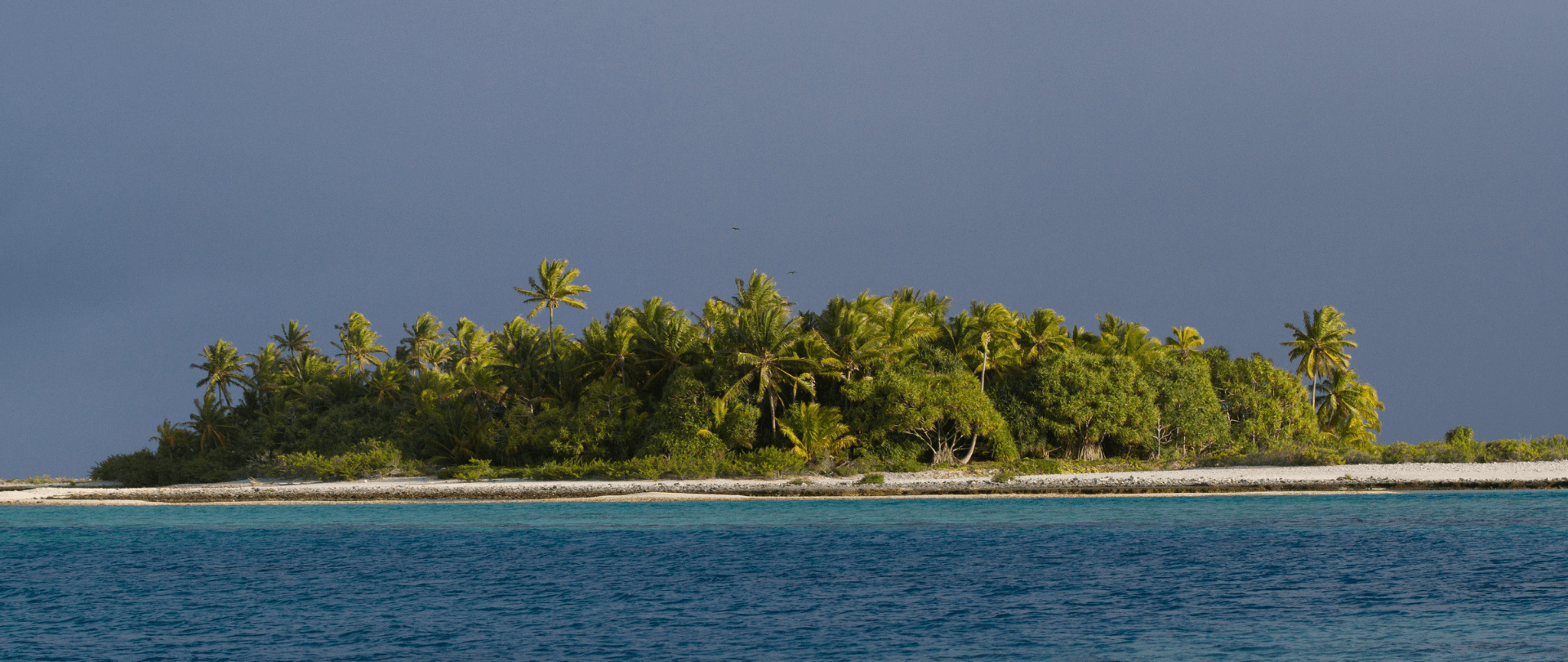
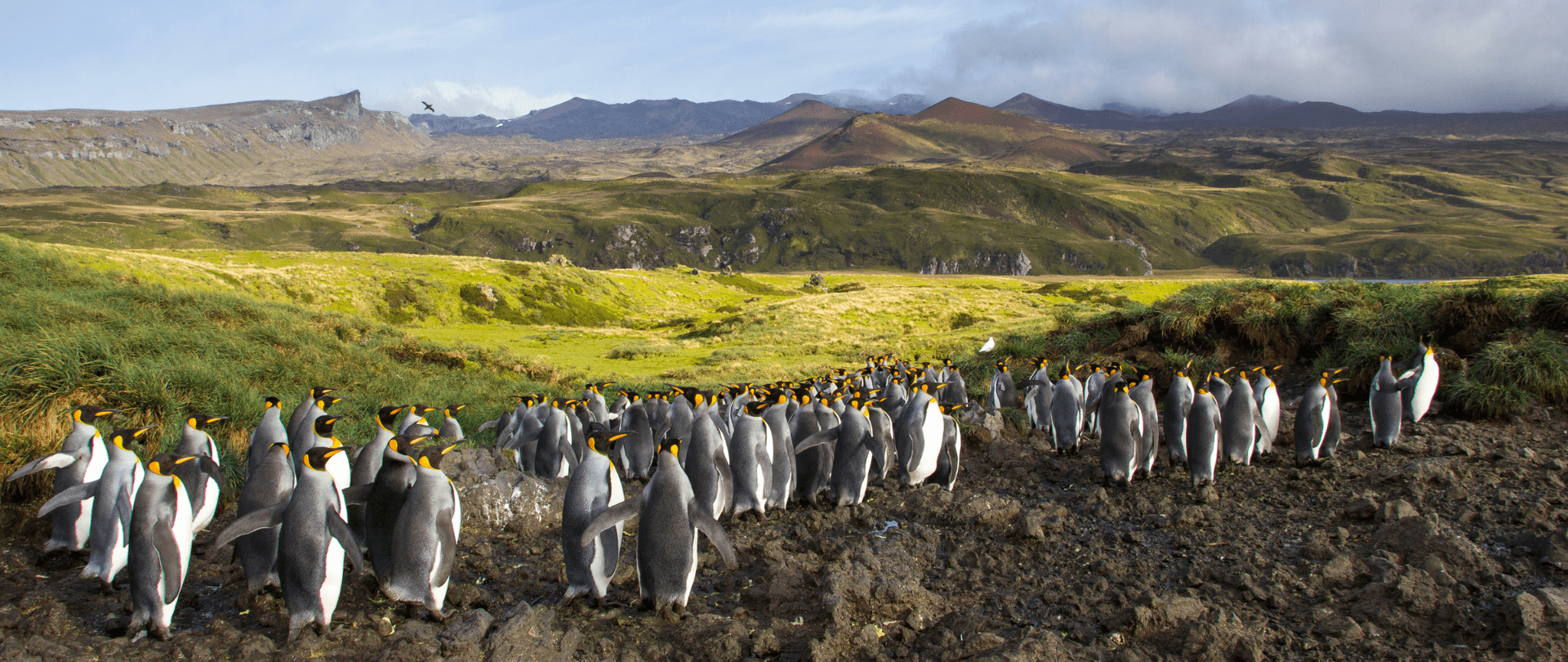
Join us in celebrating the most amazing sights from around the world by checking out these fantastic conservation photos!

Rare will support the effort to restore island-ocean ecosystems by engaging the Coastal 500 network of local leaders in safeguarding biodiversity (Arlington, VA, USA) Today, international conservation organization Rare announced it has joined the Island-Ocean Connection Challenge (IOCC), a global effort to…

Island Conservation accepts cryptocurrency donations. Make an impact using your digital wallet today!

For Immediate Release Conservation powerhouse BirdLife South Africa has joined the Island-Ocean Connection Challenge (IOCC) – a global initiative aiming to restore, rewild and protect islands, oceans and communities – to support its work to save internationally significant albatross populations…