The Ebiil Society: Champions of Palau
Ann Singeo, founder of our partner organization the Ebiil Society, shares her vision for a thriving Palau and a flourishing world of indigenous science!
Our new online shop is live!
Published on
November 1, 2017
Written by
Island Conservation
Photo credit
Island Conservation

By: Eileen Drage O’Reilly
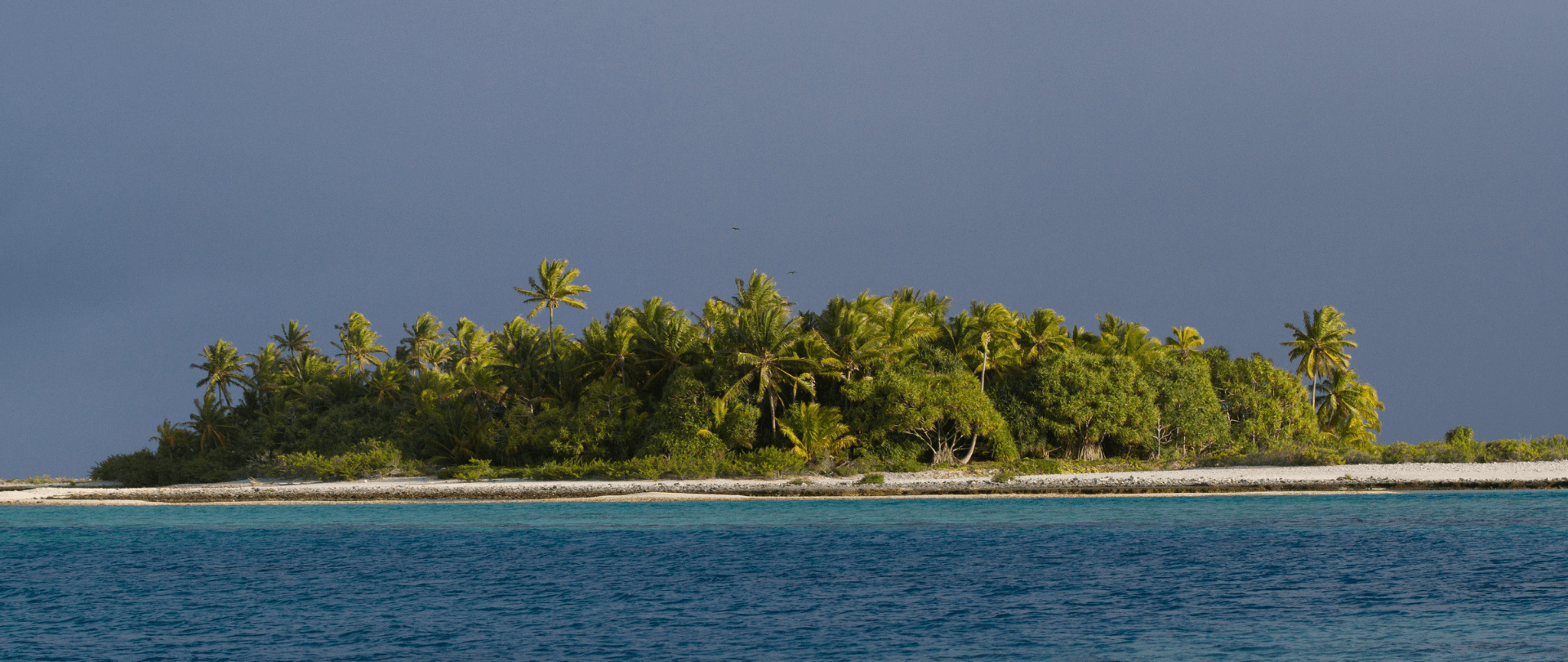
In order to halt species extinction, researchers are suggesting conservation efforts should focus on islands, which hold 41% of the world’s known highly threatened vertebrates, per a study published recently in Science Advances.
Why this matters: Lead Author and Conservation Biologist at Island Conservation, Dena Spatz explains:
Not only are species lost forever, never to be enjoyed or seen again, the decline of biodiversity has also affected human health, economics, food security, etc.
What they did: The team reviewed more than 1,000 datasets and consulted more than 500 experts worldwide.
What they found: “While islands make up only 5.3% of the earth’s landmass, they are home to 41% of the world’s highly threatened vertebrates. A disproportionate amount of threatened species,” she says. Spatz, currently at the non-profit Island Conservation, says she finds it interesting that 95% of all the threatened species in the dataset occurred on at least one island with an invasive vertebrate. Islands with the most highly threatened vertebrate populations include Madagascar, Sri Lanka, Hispaniola and Cuba.
Good news: Dena Spatz comments:
While this may seem daunting, the good news is that there are proven techniques for dealing with the threat of invasive species…and thus management of invasives on these islands could benefit 39% of the Earth’s highly threatened vertebrates.
More perspective: Robert Fisher, a conservation biologist with the U.S. Geological Survey, points out the study is based on highly threatened vertebrates as classified by the IUCN’s Red List, which is incomplete. Fisher, who was not part of this study, says that IUCN so far has only assessed roughly 40,000 out of 61,000 vertebrates and the list does not include species that may be labeled as “data deficient” because they were only assessed once. “We should be investing a lot of money in exploration and discovery right now” to better determine which species are threatened, Fisher tells Axios.
Still, Fisher says the database is a good baseline tool in fighting the extinction of species, which has “cascading effects.” An example of this is on Guam, where brown tree snakes were introduced and killed birds, which led to a huge increase in spider populations.This damaged tourism centered around birdwatching on the island and prompted concerns snakes could similarly invade Hawaii.
Featured Photo: A Critically Endangered Polynesian Ground Dove. Credit: Marie-Helene Burle/Island Conservation
Originally Printed in Axios
Check out other journal entries we think you might be interested in.

Ann Singeo, founder of our partner organization the Ebiil Society, shares her vision for a thriving Palau and a flourishing world of indigenous science!

This historic agreement aims to protect the marine and coastal areas of the Southeast Pacific.

Our projects to restore key islets in Nukufetau Atoll forecast climate resilience and community benefits in Tuvalu!

Island Conservation and partners have published a new paper quantifying ecosystem resilience on restored islands!

Climate Week NYC: what is it and why is it important? Read on to find out why Island Conservation is attending this amazing event!

With sea levels on the rise, how are the coastlines of islands transforming? Read on to find out how dynamic islands really are!
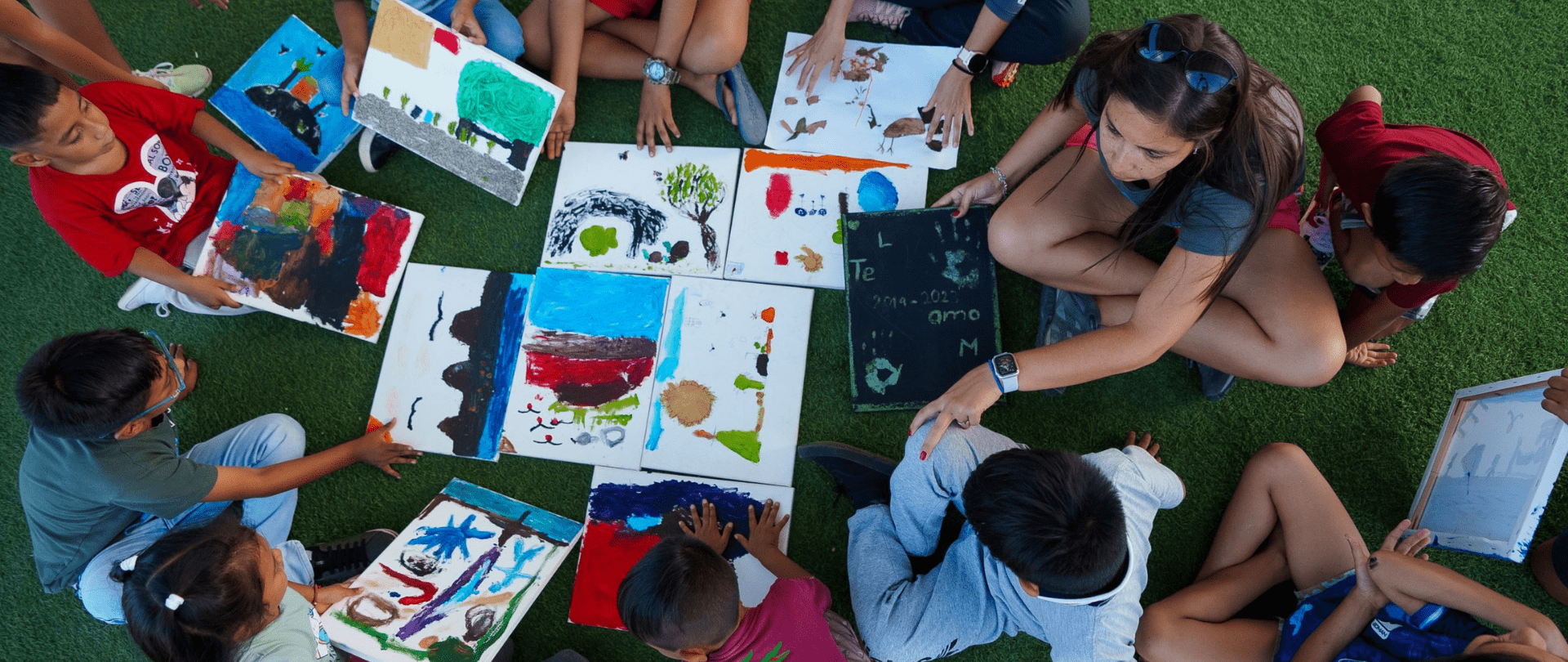
Join us in celebrating the most amazing sights from around the world by checking out these fantastic conservation photos!

Rare will support the effort to restore island-ocean ecosystems by engaging the Coastal 500 network of local leaders in safeguarding biodiversity (Arlington, VA, USA) Today, international conservation organization Rare announced it has joined the Island-Ocean Connection Challenge (IOCC), a global effort to…

Island Conservation accepts cryptocurrency donations. Make an impact using your digital wallet today!

For Immediate Release Conservation powerhouse BirdLife South Africa has joined the Island-Ocean Connection Challenge (IOCC) – a global initiative aiming to restore, rewild and protect islands, oceans and communities – to support its work to save internationally significant albatross populations…